Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2026-01-29 Origin: Site









Can fiberglass mould really be molded? This versatile material is used across industries for its ability to be shaped into complex, durable forms. From automotive to aerospace, fiberglass mould combines strength with lightweight properties. In this article, we will explore how fiberglass mould is molded, the methods used, and its many applications.
Fiberglass molding refers to the process of shaping fiberglass resin and glass fibers into a particular form by using molds. The process involves creating a master pattern or "plug," which serves as a negative or positive form for molding the final part. By applying layers of fiberglass and resin to this mold, a solid, durable, and customized part is created once the material cures. This table lists the common raw materials used in fiberglass molds and their properties, helping you understand the role of each ingredient in the mold.
Material | Type | Function and Characteristics | Technical Specifications |
Silica Sand | Inorganic Material | Provides the main component for fiberglass, enhancing strength and durability | Particle size: 80 mesh and above; Content: 55%-70% |
Limestone | Inorganic Mineral | Lowers the melting point of glass, improving strength | Chemical composition: Mainly calcium, silicon, aluminum, iron |
Soda Ash | Inorganic Salt | Lowers the melting temperature, enhancing glass fluidity | Content: 20%-25%; Sodium content: 60%-65% |
Alumina | Aluminum Ore | Improves chemical resistance, increasing anti-corrosion properties | Purity: 90%-95%; Particle size: 60-70 mesh |
Phosphate | Inorganic Compound | Enhances fire resistance and high-temperature properties | Content: 4%-6%; Purity: 98% and above |
The process of molding fiberglass begins with creating a plug, which acts as the master model or prototype. Once the plug is complete, it is coated with a release agent to prevent the fiberglass from sticking. After this, a gelcoat is applied, which serves as a protective and smooth exterior finish. Layers of fiberglass cloth or mat are then added to the mold, each layer being saturated with resin. Once the resin cures, the fiberglass hardens into the shape of the mold. The curing process involves either room temperature curing or accelerated curing using heat. The result is a strong, rigid fiberglass part that can be used in a variety of applications.
Fiberglass is a popular choice for molding due to its unique combination of properties. It is lightweight yet strong, offering a remarkable strength-to-weight ratio that rivals metals like steel. Additionally, fiberglass is highly resistant to corrosion, making it ideal for use in harsh environments, such as marine or chemical industries. Its flexibility in molding allows for the creation of complex shapes, enabling it to meet custom design needs. Fiberglass also has high dimensional stability, meaning it maintains its shape and size even when exposed to temperature changes. These characteristics, combined with its durability and cost-effectiveness, make fiberglass an ideal material for molding.
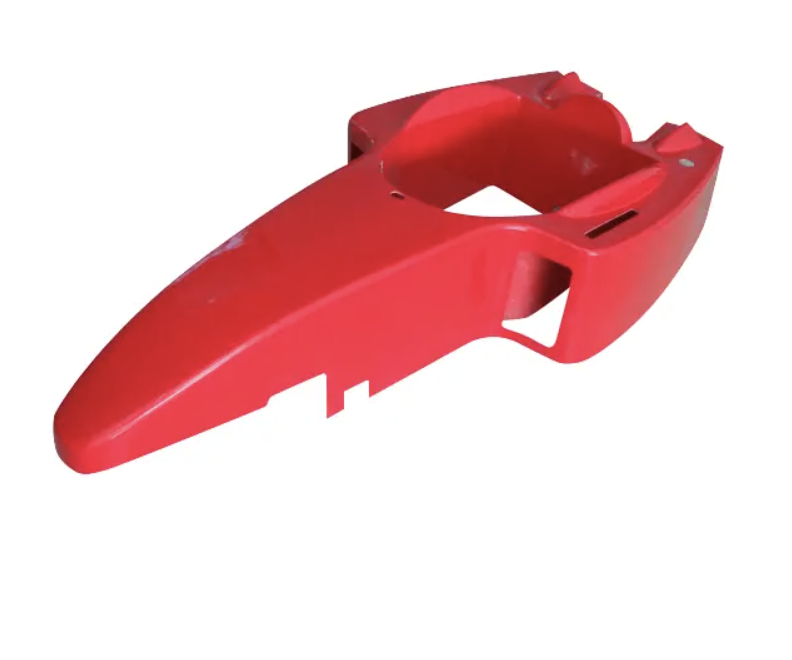

The creation of the plug is the first step in making a fiberglass mold. A plug is a precise replica of the intended final product, and it must be made from materials that are rigid, dimensionally stable, and smooth. Common materials used for plugs include foam, wood, or clay. Foam is often used for larger items because it is lightweight and easy to shape, while wood or clay can provide more stability for intricate designs. Once the plug is made, it must be prepared by filling any imperfections and sanding it smooth. A well-prepared plug is crucial for ensuring a high-quality final product.
After the plug is ready, the next step is to prepare the mold. This involves applying a release agent, such as wax or a chemical release spray, to ensure that the fiberglass does not stick to the plug. The release agent helps the mold separate from the plug easily once the fiberglass has cured. In some cases, a layer of gelcoat is applied first, creating a glossy, durable finish on the exterior of the mold. Once the release agent or gelcoat has been applied, the mold is ready for the fiberglass layering process.
In the fiberglass molding process, using the right gelcoat ensures that the final product has a smooth and durable surface, which is essential for both aesthetic appearance and performance. The following table outlines the common types of gelcoats and their properties, providing application tips to ensure optimal results.
Gelcoat Type | Application Area | Characteristics and Uses | Technical Specifications |
Tooling Gelcoat | Mold production, specific parts' exterior surface | Provides a smooth and corrosion-resistant surface | Viscosity: 1500-2000 cps; Hardness: D60-D65 |
Polyester Gelcoat | Automotive, Marine | Offers good gloss and chemical resistance, ideal for high surface quality requirements | Curing time: 30 minutes; Thickness: 0.6mm-2mm |
Epoxy Gelcoat | High-temperature applications, precision molds | High-temperature resistance, chemical corrosion resistance | Viscosity: 1000-1500 cps; Hardness: D55-D60 |
Wax-Free Gelcoat | Quick-curing molds | Wax-free formula to reduce wax marks, suitable for short production runs | Curing time: 15 minutes; Thickness: 0.5mm-1.5mm |
Tip:Choosing the correct gelcoat type is crucial for ensuring the mold surface is smooth and durable. Make sure the gelcoat fully cures to avoid surface defects.
Open molding is one of the most common methods for fiberglass molding, particularly for large, less complex parts. In this process, resin and fiberglass are applied by hand or spray onto a single-sided mold. Gelcoat is usually applied first, followed by layers of fiberglass that are saturated with resin. Once the resin cures, the part is removed from the mold. Open molding is cost-effective and flexible, allowing manufacturers to create a variety of large components, such as boat hulls, tanks, and industrial panels.
Closed molding involves the use of a two-sided mold, which can be either clamped or sealed together to create a fully enclosed space. This method is typically used for parts that require a smooth finish on both sides and precise dimensions. Resin Transfer Molding (RTM) and Compression Molding are examples of closed molding techniques. In RTM, resin is injected into the mold under low pressure, ensuring a consistent flow of resin throughout the mold. Compression molding, on the other hand, uses heat and pressure to mold the fiberglass, producing high-quality, durable parts.
Vacuum infusion is a closed molding process that uses a vacuum to pull resin through a dry laminate. This method results in stronger, lighter parts with fewer air pockets, ensuring greater consistency and reducing material waste. Vacuum infusion is particularly useful for manufacturing parts that require high strength and low weight, such as automotive body panels or aerospace components. The vacuum pressure helps eliminate air voids and ensures a more uniform distribution of resin throughout the fiberglass layers.
One of the primary benefits of fiberglass molding is its excellent strength-to-weight ratio. Fiberglass components are lightweight yet extremely strong, making them ideal for applications where weight is a critical factor, such as in the aerospace and automotive industries. Compared to metals like steel, fiberglass can provide the same level of strength while being significantly lighter. This property helps improve fuel efficiency in vehicles and aircraft while reducing overall material costs.
Fiberglass is inherently resistant to corrosion, which makes it ideal for use in environments exposed to harsh chemicals or moisture. This makes fiberglass molds highly suitable for industries such as marine, chemical processing, and wastewater treatment. The material’s chemical resistance helps prolong the lifespan of molded products, reducing the need for maintenance and replacements. In marine applications, fiberglass's resistance to saltwater corrosion makes it the preferred choice for boat hulls and other watercraft components.
Fiberglass molding offers designers and engineers the freedom to create complex and customized shapes with high precision. Whether it’s for intricate automotive body parts or aerospace components, fiberglass can be molded into shapes that would be difficult or costly to achieve with traditional materials like metal or plastic. Its flexibility allows for the creation of custom designs that meet specific functional and aesthetic requirements, making it a preferred choice in industries where both form and function are important.
Fiberglass molding is extensively used in the marine and automotive industries to create components that require strength, durability, and lightweight properties. In the marine industry, fiberglass is used to mold boat hulls, decks, and other parts that are exposed to the elements. Fiberglass boat hulls are preferred for their resistance to corrosion and their ability to withstand the harsh conditions of the sea. In the automotive industry, fiberglass is used to create complex body panels, spoilers, and dashboards, contributing to improved fuel efficiency and reduced vehicle weight.
In the aerospace industry, fiberglass is valued for its strength-to-weight ratio and its ability to be molded into precise shapes. Components such as structural parts and wings for aircraft are often made from fiberglass to ensure they are lightweight yet strong enough to withstand the demands of flight. In construction, fiberglass is used for custom architectural facades, roofing panels, and storage tanks. Its resistance to environmental factors like moisture, UV light, and temperature variations makes it a durable and cost-effective material for construction projects.
Fiberglass molds are used to create a wide variety of consumer goods and industrial equipment. For example, fiberglass is used in the production of ergonomic furniture, sinks, and amusement park slides, as well as in tanks and pipes for water treatment. The ability to mold fiberglass into intricate shapes allows manufacturers to produce products that are both functional and aesthetically appealing. Additionally, fiberglass’s resistance to wear, impact, and chemicals makes it an ideal choice for industrial equipment that needs to withstand heavy use.
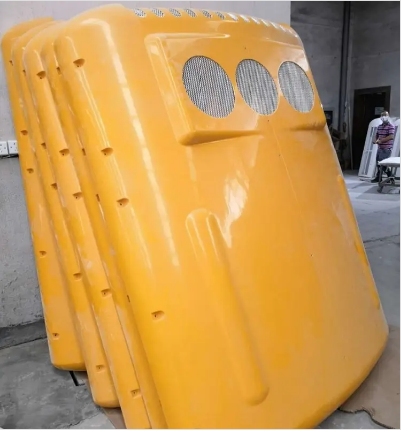

Proper maintenance of fiberglass molds is essential for ensuring their longevity and consistent performance. After each use, it is important to clean the mold thoroughly to remove any resin or fiberglass residue. A release agent, such as wax or PVA, should be reapplied before each use to ensure easy demolding. Regular cleaning and proper release agent application help maintain the mold's surface quality and prevent contamination from affecting the final product.
During the use of fiberglass molds, timely handling of imperfections and damage is critical to ensure the quality of the parts and the long-term use of the mold. This table provides methods and steps for handling common fiberglass mold imperfections, helping you maintain the mold’s long-term performance.
Imperfection Type | Repair Method | Tools/Materials | Considerations |
Cracks | Fill with resin and sand | Polyester resin, Sanding tools | Avoid excessive sanding to prevent affecting the surface smoothness |
Air Bubbles | Remove with metal roller | Metal roller, Adhesive | Ensure all bubbles are removed to prevent defects in the final molded part |
Rough Surface | Apply smoothening agent and sand | Smoothening agent, Sandpaper | Apply the smoothening agent evenly, ensuring uniform coating thickness |
Tip:Promptly repair small imperfections on the mold to extend its lifespan and ensure high-quality final products.
To ensure a mold is suitable for multiple uses, it should be properly seasoned with several layers of release agent before its first use. Additionally, after each use, the mold should be inspected for signs of wear and tear. Proper care and maintenance, including regular cleaning and application of release agents, will extend the mold’s lifespan and ensure that it continues to produce high-quality molded parts.
Fiberglass molding is a versatile and effective process for creating durable, lightweight products in industries like automotive, aerospace, and marine. It allows for complex shapes with high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent corrosion resistance. The molding process is customizable, offering flexibility for various applications. Changshu Jianan FRP Products Co., Ltd. provides high-quality fiberglass products that combine durability and cost-effectiveness, making them a valuable resource for businesses in need of reliable fiberglass solutions.
A: Yes, fiberglass can be molded into intricate and durable shapes, making it ideal for applications in various industries like automotive, aerospace, and marine. Fiberglass mould offers flexibility in design while maintaining strength.
A: The process involves creating a plug, applying gelcoat, layering fiberglass cloth with resin, and curing. This allows the creation of strong, precise fiberglass mould products suitable for many industries.
A: Fiberglass mould is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and highly durable, making it ideal for producing long-lasting parts in industries that require custom shapes and high performance.
A: Fiberglass mould offers a superior strength-to-weight ratio compared to metals like steel, making it lighter and more efficient for applications in aerospace, automotive, and marine industries.
A: Yes, fiberglass mould is highly resistant to corrosion, making it ideal for marine, chemical, and other industries that deal with harsh environments and exposure to moisture and chemicals.
A: The curing time for fiberglass mould varies depending on the method used, typically ranging from several hours to a day, depending on temperature and resin type.
+86 13913647707 / 13915651436