Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2026-07-07 Origin: Site









When it comes to selecting the right material for your building projects, understanding the key differences between fiberglass panels and polycarbonate sheets is crucial. Both materials are frequently used in construction, roofing, partitions, and other applications, but each has distinct advantages and limitations. This article will explore the fundamental differences between these two materials, helping you make an informed decision based on your project's needs.
Fiberglass panels are made from glass fibers that are woven together and bonded with a resin to form a sturdy and versatile material. This composition makes fiberglass an excellent choice for applications requiring high strength and flame resistance. Common uses of fiberglass panels include roofing, partitions, and insulation in industrial settings.
Key Features: Fiberglass is known for its flame resistance, good tensile strength, and availability in a wide range of colors and patterns. However, fiberglass panels tend to degrade when exposed to UV rays, causing yellowing and a reduction in overall aesthetic quality over time.
Applications: Fiberglass panels are primarily used in interior applications or areas where direct sunlight and UV exposure are limited. They are not ideal for outdoor environments that require long-term durability or clarity.
Polycarbonate sheets are a type of thermoplastic made from synthetic polymer. They are clear, durable, and UV resistant, making them a popular choice for outdoor projects. Polycarbonate sheets can be manufactured in various forms, such as clear, translucent, or opaque, depending on the required light transmission.
Key Features: Polycarbonate sheets are incredibly strong, up to 200 times stronger than glass of the same thickness, and they have excellent resistance to both impact and weathering. Additionally, polycarbonate is naturally UV resistant, and with added UV coatings, the material can retain its color and clarity for many years.
Applications: Polycarbonate sheets are commonly used in roofing, skylights, patio covers, and even windows. Their superior impact resistance makes them suitable for areas prone to hailstorms or heavy weather conditions.
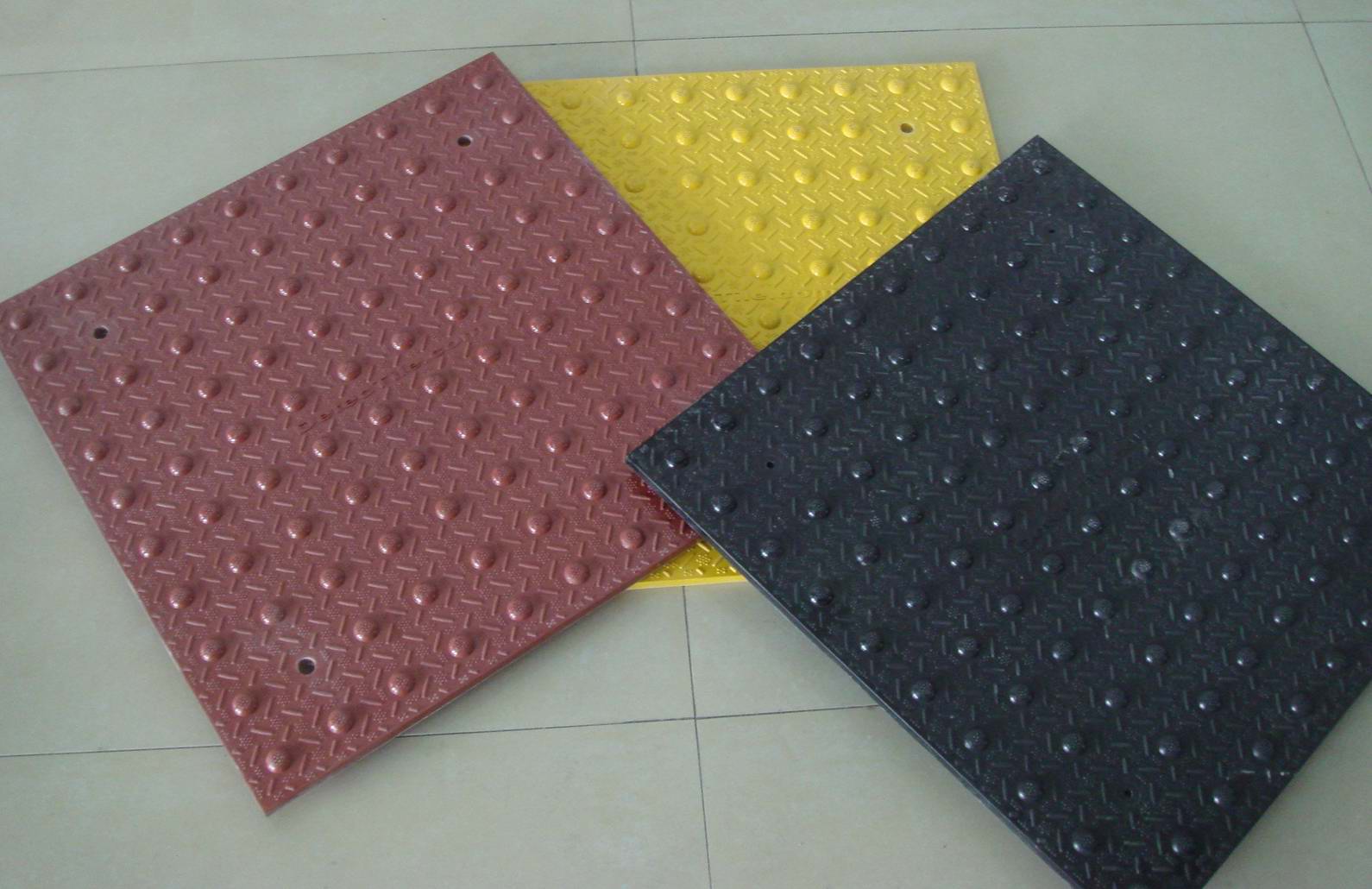

Polycarbonate Sheets: Polycarbonate is highly durable and resistant to impacts, making it ideal for projects that will experience heavy wear or high stress. Whether it's used for skylights, roofs, or other structural applications, polycarbonate is much stronger than glass and can endure impacts that would otherwise break other materials. This strength, combined with its lightweight nature, reduces the need for heavy support structures, making it cost-effective in the long term.
Fiberglass Panels: While fiberglass is also durable, it does not have the same level of impact resistance as polycarbonate. Fiberglass can crack or become brittle under heavy stress, especially if it is exposed to UV rays for extended periods. This makes fiberglass a less suitable option for high-impact applications or outdoor environments with extreme weather conditions.
Polycarbonate Sheets: One of the biggest advantages of polycarbonate sheets is their ability to withstand UV rays. Most polycarbonate sheets are manufactured with a UV coating, which prevents the material from yellowing, discoloring, or degrading over time. This makes polycarbonate an excellent choice for applications exposed to direct sunlight.
Fiberglass Panels: Fiberglass panels, on the other hand, are highly susceptible to UV damage. Over time, the UV rays cause the material to discolor and lose its clarity. Clear fiberglass panels often turn yellow, which can make them less visually appealing and impact their effectiveness, especially in applications where transparency is important.
Polycarbonate Sheets: Polycarbonate sheets are highly resistant to heat, making them suitable for environments with fluctuating or high temperatures. This heat resistance also contributes to their longevity and effectiveness in harsh weather conditions, where other materials might fail.
Fiberglass Panels: Fiberglass is less heat-resistant than polycarbonate and can start to degrade under high-temperature conditions. The resin bonding the fiberglass can weaken in extreme heat, causing the material to warp, crack, or lose its structural integrity.
Polycarbonate Sheets: Polycarbonate is significantly lighter than glass and fiberglass, which makes it easier and less expensive to install. The reduced weight of polycarbonate allows for the use of lighter and cheaper framing systems, which contributes to overall cost savings during installation.
Fiberglass Panels: Fiberglass panels are heavier than polycarbonate, which means they often require stronger support structures. This added weight increases the cost and complexity of the installation process. In applications where weight is a crucial factor, polycarbonate is the preferred choice.
Polycarbonate Sheets: Polycarbonate sheets are generally more affordable than fiberglass, especially when you factor in the long-term benefits such as UV resistance and minimal maintenance costs. While polycarbonate might have a higher upfront cost compared to fiberglass, the overall lifetime cost is lower due to its durability and low maintenance.
Fiberglass Panels: Fiberglass panels tend to be more expensive than polycarbonate, particularly when considering the cost of installation and ongoing maintenance. The material itself can be more costly, and frequent repairs or replacements due to UV degradation can add to the overall expense.
Polycarbonate Sheets: Polycarbonate sheets provide significant long-term savings because they require minimal maintenance and are highly durable. They can last for over 10 years with proper care, offering excellent value over time.
Fiberglass Panels: Fiberglass requires more frequent maintenance, particularly in outdoor settings where UV degradation is a concern. It may need to be replaced or repaired every few years, leading to higher overall costs over its lifespan.
Polycarbonate is recyclable, and many manufacturers are now using more sustainable production methods to reduce its environmental impact. However, because it is a plastic material, it can still contribute to plastic waste if not disposed of properly. Polycarbonate sheets that are made from recycled materials can offer a more eco-friendly option for construction projects.
Fiberglass is more challenging to recycle due to the resin bonding process. While it is durable and long-lasting, the inability to easily recycle fiberglass poses a significant environmental challenge. Additionally, fiberglass production can create pollutants if not done sustainably. It's important to consider the life cycle of fiberglass panels when evaluating their environmental footprint.
Polycarbonate sheets are perfect for outdoor applications where strength, UV resistance, and impact resistance are critical. Common uses include:
Roofing for patios, decks, and commercial buildings
Skylights and light panels for natural lighting
Protective barriers and storm-resistant windows
Fiberglass is better suited for interior applications where UV exposure is minimal. It's often used for:
Indoor partitions and dividers
Insulation in industrial settings
Non-load-bearing applications that don't require high impact resistance
For roofing applications, polycarbonate sheets are the clear winner due to their:
UV resistance
Impact resistance
Ability to remain clear over time
Fiberglass panels, while useful in certain situations, are not suitable for long-term outdoor roofing applications due to their tendency to yellow and degrade under UV exposure.
Polycarbonate sheets require minimal maintenance, mostly consisting of occasional cleaning to remove dirt and debris. Their UV resistance means they won't require constant repair or replacement like fiberglass.
Fiberglass requires regular inspection and maintenance. If used in outdoor applications, it will need to be cleaned frequently to prevent buildup and mitigate the effects of yellowing. The material's exposure to UV rays can also lead to degradation, which may require repairs or replacement.
In conclusion, while both fiberglass panels and polycarbonate sheets have their respective advantages, polycarbonate is generally the better choice for most outdoor applications due to its strength, UV resistance, and longevity. Fiberglass, on the other hand, can still be a viable option for interior or low-impact projects where UV exposure is limited.Consider the specific needs of your project—whether it's roofing, partitions, or a different construction application—to determine which material is best for you.

Yes, polycarbonate sheets are widely used for windows due to their strength and light transmission properties. They are an excellent alternative to glass for applications where safety and durability are a priority.
A:Fiberglass panels are resistant to water, making them suitable for environments where water exposure is a concern. However, prolonged exposure to water and UV rays can eventually degrade the material.
A:Polycarbonate sheets can last for over 10 years with proper care. Their UV coating and durable nature make them ideal for long-term outdoor use.
A:Yes, in some cases, both materials can be used in different parts of a project, such as using polycarbonate for roofing and fiberglass for partitions.
+86 13913647707 / 13915651436