Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-07-31 Origin: Site










As electric vehicles (EVs) surge toward 30% global market penetration by 2030, a quiet revolution brews in China’s factories. Here, fiberglass-reinforced plastic (FRP) body components—once niche substitutes—now form the core of lightweight strategies for Tesla, BYD, and NIO. This article dissects China’s 180-billion-yuan FRP ecosystem, where material science meets policy ambition to redefine automotive manufacturing.
Market control: China supplies 70% of global unsaturated polyester resin, with Sinopec and Changzhou Tianma leading production. Bio-based resins (soy/linseed oil derivatives) now comprise 15% of output, reducing carbon footprint by 40%.
Tech shift: Vinyl ester resins—critical for battery enclosures—grow at 12% CAGR, driven by corrosion resistance demands in EVs.
Scale: China consumed 800,000 tons of glass fiber in 2024, 60% for automotive use. Jushi Group and Taishan Fiberglass dominate, with costs 20% lower than Western peers.
Recycling gap: Only 10% of FRP waste is recycled due to limited pyrolysis facilities—a focus of Beijing’s 2025 Circular Economy Plan.
Table: Key Raw Material Suppliers
| Material | Top Chinese Suppliers | Global Market Share |
|---|---|---|
| Glass Fiber | Jushi Group, Taishan Fiberglass | 65% |
| Polyester Resin | Sinopec, Changzhou Tianma | 70% |
| Carbon Fiber | Zhongfu Shenying, Hengshen | 28% |
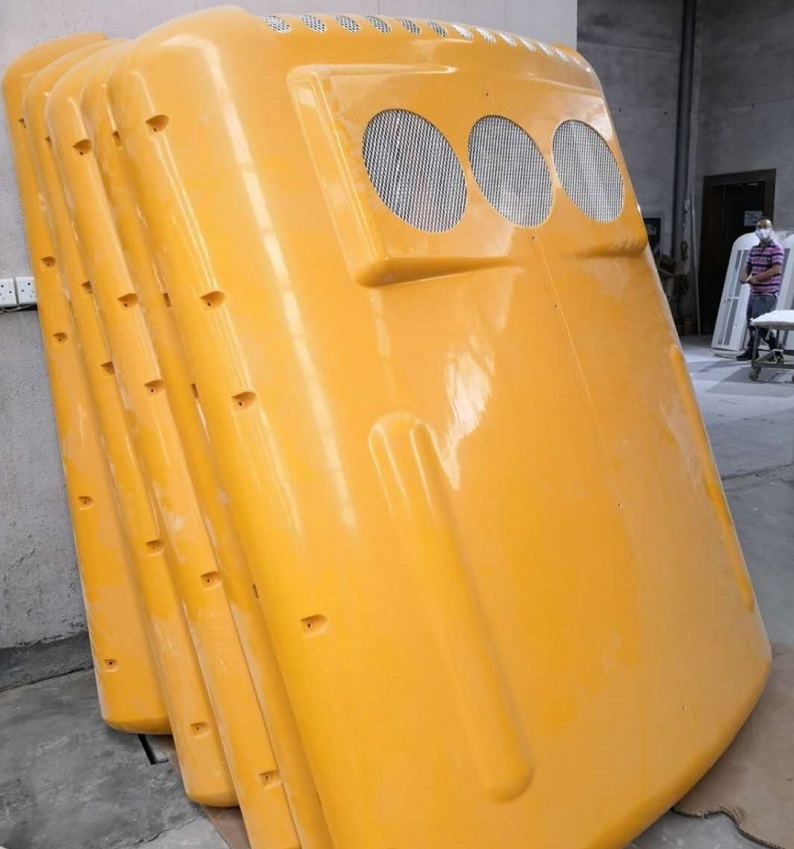
RTM dominance: 60% of Chinese FRP parts use resin transfer molding, cutting cycle times to 30 minutes (vs. 2 hours for hand lay-up). Jianan’s automated lines produce 50,000 bus AC covers/year with <0.5% defect rates.
T-RTM breakthrough: BASF-KraussMaffei’s thermoplastic RTM enables recyclable B-pillars for Volkswagen, slashing CO₂ emissions by 30% vs. thermosets.
Mold engineering: Over 200 specialized firms (e.g., Shanghai FRP Research) create combo molds for complex geometries (e.g., integrated fender-lighting units). AI-driven flow simulation cuts prototyping costs by 40%.
Customization: Jianan’s modular molds support low-volume runs (500–5,000 units)—ideal for EV startups like NIO’s 20,000-unit ES6 roof panel orders.
Market concentration: Shanghai FRP Research Institute and Jiangsu Huayi command 60% share in structural parts. Niche players (e.g., Jianan) dominate regional bus/truck segments with hyper-localized supply chains.
Profit margins: High-volume RTM parts yield 15–20% margins, while custom designs (e.g., integrated battery trays) reach 30%.
ASEAN expansion: Thailand’s EV 3.0 policy fuels 25% annual growth in FRP part imports. Jianan’s fiberglass roof boxes for pickup trucks hold 30% market share in Thailand.
Europe’s recycling pivot: EU ELV Directive compliance drives demand for T-RTM parts—China’s bio-resin B-pillar exports surged 45% in 2024.
Targets: MIIT’s 2025 goal mandates 35% lightweight material adoption in EVs, with FRP comprising 50% of non-structural parts.
Fiscal incentives: VAT cuts (13% → 9%) + direct subsidies (up to ¥50,000 per EV using domestic FRP).
Belt and Road Initiative: FRP part exports to Kazakhstan/Uzbekistan grew 70% in 2024—key for bus/truck bodies in extreme climates.
Standards diplomacy: China’s GB/T 38534-2020 FRP corrosion standard adopted as ASEAN benchmark, displacing ISO.
Solvolysis pilots: Sinopec’s plant recovers 85% glass fiber from scrap bumpers—cutting virgin material use by 30%.
3D-printed molds: Reduce lead times for complex parts (e.g., aerodynamic skirts) from 12 weeks to 72 hours.
Resin flow prediction: Alibaba Cloud’s algorithm minimizes voids in RTM parts, boosting strength by 15% and reducing waste.
Digital twins: Real-time monitoring of 10,000+ mold parameters slashes downtime by 40% at Jiangsu Huayi.
Price risks: Glass fiber costs fluctuate 20% quarterly with energy prices. Local governments now stockpile to stabilize supply.
Workforce gap: Shortfall of 50,000 skilled RTM technicians—vocational training partnerships (e.g., Foxconn-Jianan Academy) address this.
US/EU response: GM’s patented FRP-metal hybrid roofs (CN114852180B) target 25% weight reduction—countering Chinese cost advantages.
Tariff threats: EU anti-dumping probes may impose 15% duties on Chinese FRP parts by 2026.
Q: Why is China dominant in FRP body parts?
A: Unmatched resin/fiber scale, policy support (e.g., tax breaks), and RTM automation—producing parts 30% cheaper than EU/US.
Q: Can Chinese FRP meet EU crash standards?
A: Yes. Jianan’s bus roofs pass ECE R66 rollover tests at 1.5x load capacity—equal to steel but 50% lighter.
Q: How do tariffs impact global supply chains?
A: ASEAN factories (e.g., Jianan’s Thailand plant) now assemble Chinese FRP semi-finished goods to bypass EU/US duties.
Q: Is FRP recycling feasible at scale?
A: Partially. Solvolysis recovers fibers but costs 2x virgin production—scale-up via Sinopec’s 2026 mega-plant aims to close the gap.
China’s FRP ecosystem—ed by state ambition, manufacturing agility, and raw material hegemony—has positioned itself as the indispensable engine of global automotive lightweighting. As T-RTM and AI democratize high-performance composites, the industry’s next leap will hinge on conquering recycling and talent gaps. For automakers worldwide, ignoring China’s FRP revolution is no longer an option.
+86 13913647707 / 13915651436